The Safety of PRP Treatment: A Comprehensive Examination
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy has emerged as a revolutionary approach in regenerative medicine, offering promising outcomes in various medical and cosmetic applications. From orthopedics and sports medicine to dermatology and aesthetic procedures, PRP has gained widespread popularity for its potential to stimulate tissue repair and promote healing. However, as with any medical intervention, concerns regarding safety remain paramount. In this comprehensive examination, we delve deep into the safety profile of PRP hair treatment in Dubai(حقن البلازما للشعر في دبي), exploring the scientific evidence, clinical experience, and emerging perspectives to provide a nuanced understanding of its risks and benefits.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding PRP Therapy:
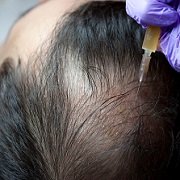
PRP therapy involves the extraction and concentration of platelets from the patient’s own blood, which are then reintroduced into the body at the site of injury or treatment. Platelets are rich in growth factors, cytokines, and other bioactive substances that play a pivotal role in tissue regeneration and wound healing. The process typically begins with a simple blood draw, followed by centrifugation to separate the platelet-rich plasma from other blood components. The concentrated PRP is then administered via injection or topical application, depending on the specific medical or cosmetic indication.
Safety Considerations:
- Autologous Nature: One of the key factors contributing to the safety of PRP therapy is its autologous nature. Since PRP is derived from the patient’s own blood, the risk of allergic reactions, immune rejection, and transmission of infectious diseases is significantly reduced. This inherent biocompatibility makes PRP an attractive option for regenerative treatments.
- Minimally Invasive Procedure: PRP treatment is minimally invasive and is typically performed as an outpatient procedure in a medical office or clinic setting. The injections are administered using fine needles, and adverse events such as bleeding, infection, or scarring are rare when performed by qualified healthcare professionals. Patients can usually resume their normal activities shortly after the procedure, with minimal downtime.
- Low Risk of Side Effects: Clinical studies evaluating the safety of PRP therapy have consistently reported a low incidence of adverse effects. Common side effects, such as mild pain, swelling, or bruising at the injection site, are usually transient and resolve spontaneously within a few days. Serious complications are rare but can include infection, nerve damage, or tissue damage if proper sterile technique is not followed during the procedure.
- Individual Variation: It’s important to recognize that the safety and efficacy of PRP therapy may vary depending on individual patient factors, including underlying health conditions, medication use, and treatment technique. Patients should undergo a thorough evaluation and discuss potential risks with their healthcare provider before undergoing PRP treatment to ensure personalized care and optimal outcomes.
Scientific Evidence:
Numerous clinical studies have investigated the safety profile of PRP therapy across various medical specialties. In orthopedics and sports medicine, PRP therapy has been extensively studied for its role in the management of musculoskeletal injuries, such as tendonitis, ligament tears, and osteoarthritis. Meta-analyses and systematic reviews have generally concluded that PRP treatment is safe, with minimal risk of adverse events compared to traditional interventions such as corticosteroid injections or surgery.
In dermatology and aesthetic medicine, PRP therapy is commonly used for facial rejuvenation, scar revision, and hair restoration. Clinical trials and observational studies have reported high patient satisfaction rates and low rates of complications following PRP treatment for these indications. Adverse events such as infection or allergic reactions are rare but can occur, particularly if proper sterile technique is not followed during the preparation and administration of PRP.
Future Directions:
While the current evidence supports the safety and efficacy of PRP therapy in various clinical settings, ongoing research continues to explore new applications and optimize treatment protocols. Advances in biotechnology, such as platelet-rich fibrin (PRF) and exosome therapy, hold promise for further enhancing the regenerative potential of PRP treatment. Additionally, efforts to standardize PRP preparation techniques and dosage guidelines aim to ensure consistency and reproducibility across different healthcare settings.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, PRP therapy represents a safe and promising approach in regenerative medicine, offering patients a natural and minimally invasive option for promoting tissue repair and regeneration. While the overall safety profile of PRP treatment is favorable, it is essential for patients to undergo thorough evaluation and receive treatment from qualified healthcare professionals to minimize the risk of complications. By adhering to established protocols and guidelines, healthcare providers can maximize the safety and efficacy of PRP therapy, providing patients with an effective means of improving their health and quality of life. As research continues to advance and technology evolves, the future of PRP therapy holds great potential for transforming the landscape of regenerative medicine and enhancing patient care worldwide.